- How Is A Nerve Impulse Transmitted Across A Synapse Without
- How Does A Synapse Transmit A Nerve Impulse
- Steps Of Nerve Impulse
A nerve impulse is only transmitted across the synapse. If enough neurotransmitter is released. Weak stimuli don't reach this critical number. Weak stimuli don't reach this critical number. Transmission of Nerve Impulse across Synapse. Impulse travels down the axon of a presynaptic neuron. Reaches the synaptic end bulb and opens voltage sensitive Ca 2+ channels. Calcium enters the cell and through a series of reactions, cause the synaptic vesicles to fuse to cell membrane. Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. Feb 21, 2021 A synapse is the small gap between two neurons, where nerve impulses are relayed by a neurotransmitter from the axon of a presynaptic (sending) neuron to the dendrite of a postsynaptic (receiving) neuron. It is referred to as the synaptic cleft or synaptic gap. A nerve impulse is transmitted to another cell at either an electrical or a chemical synapse. What causes the transmission of a nerve impulse? The transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of electrical changes across the membrane of the neuron.
What is Synapse?
A nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another through junctions called synapses. A synapse is formed by the membranes of a pre-synaptic neuron and a post-synaptic neuron, which may or may not be separated by a gap called synaptic cleft. There are two types of synapses, namely, electrical synapses. Chemical synapses.
Atmdesk driver download for windows 10. Synapse(also called interneural) is the connection between the axon of one neuron and the dendron of other neuron having a gap of 200 Å. Nerve Impulses travel from axon to dendron as one-way traffic or unidirectional transmission.
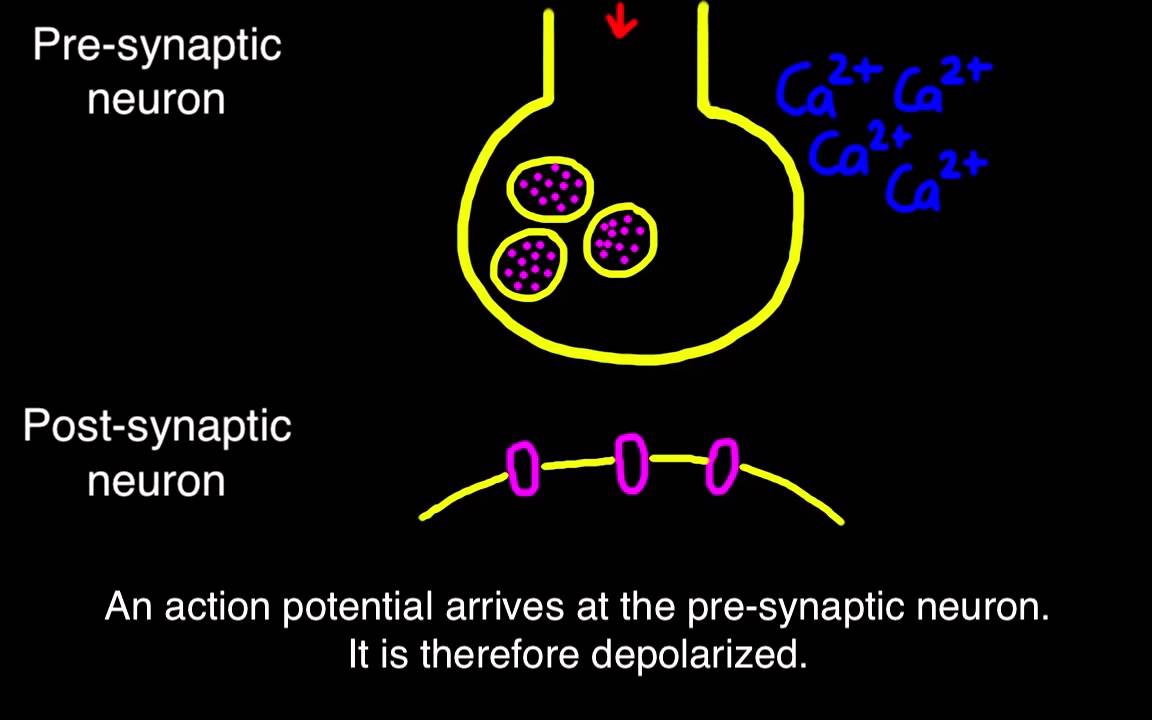
The end of the axon forms the pre-synaptic neuron (before synapse) and the tip of the dendron forms the post-synaptic neuron (after synapse). Kohjinsha laptops & desktops driver download. Ends of pre-synaptic ganglion are enlarged to form synaptic knob/button are separated from post-synaptic ganglion by a narrow passage (200 Å) called synaptic cleft filled with synaptic fluid.
Nerve Impulse is transmitted across the Synapse:
How Is A Nerve Impulse Transmitted Across A Synapse Without
There are two types of synapses i.e. chemical and electrical, depending upon the nature of the transfer of information across the synapse.
Chemical Synapse:

How Does A Synapse Transmit A Nerve Impulse
The axon terminal divides into many branches and each ends into a synaptic knob. The synaptic knob of each axon comes in contact with the dendrite of the next neuron. The synaptic knob contains many synaptic vesicles in its cytoplasm and these vesicles store chemicals such as norepinephrine and acetylcholine (neurotransmitter). The membrane of the synaptic knob on the axon side is thickened due to cytoplasmic condensation and is called a presynaptic membrane. When a wave of depolarization reaches the presynaptic membrane, Ca2+ ions diffuse into the terminal from the surrounding fluid. The Ca2+ ions then stimulate synaptic vesicles in the terminal to move to the terminal membrane, fuse with it and then rupture vesicles for release of neurotransmitter into the cleft. These are then diffused into the synaptic gap (about 20 nanometres). They then combine with specific receptor molecules of the target cell or receiving cells dendrites, which is called the postsynaptic membrane. They cause sparking a second electrical current due to depolarization, passing on its signal. This results in the propagation of nerve impulse in the next neuron. To end the signal, the synaptic lobes reabsorbs some neurotransmitters and enzymes in the synapse neutralize others. In a chemical synapse, the nature of messenger neurotransmitter remains different in different synapses, thus permitting different kind of responses.
Electrical Synapse:
Steps Of Nerve Impulse
These synapses are specialized for rapid signal transmission. Mediatek network & wireless cards driver. The cells are separated by a gap, the synaptic cleft, of only 0.2 nanometres so that an action potential arriving at the pre-synaptic side of the cleft can sufficiently depolarize the post-synaptic membrane to directly trigger its action potential.
